2025 Education ERP Market Expansion: Growing to $24.5 Billion with Digital Transformation in U.S., China, and India
Discover how Trump’s presidency influences Education ERP markets in 2025, with a focus on US, China, and India’s leadership. This comprehensive analysis explores market trends, technological innovations, and policy impacts shaping the future of educational technology across these major economies. Learn about key players, challenges, and opportunities in this rapidly evolving sector.
- Last Updated:
Education ERP Market: Q1 and Q2 2025 Predictions
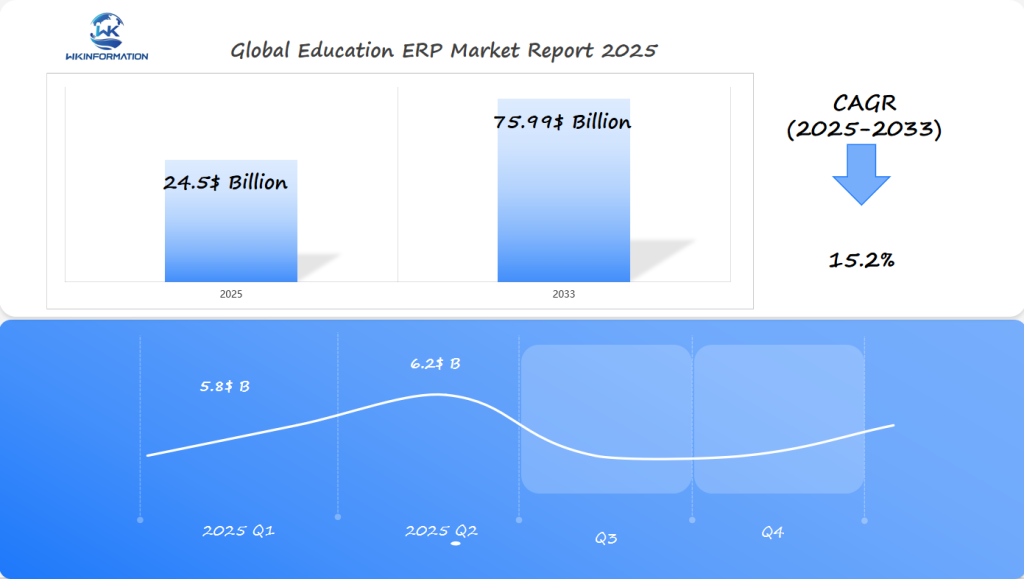
The Education ERP market is expected to reach approximately USD 24.5 billion in 2025, driven by the growing adoption of digital solutions in educational institutions.
In Q1 2025, the market is predicted to generate around USD 5.8 billion, accounting for roughly 24% of the annual market value. The demand for advanced ERP systems in schools, universities, and online learning platforms in regions like the U.S., China, and India will fuel this initial surge. By Q2 2025, the market is expected to grow further, reaching approximately USD 6.2 billion, as educational institutions continue to digitalize operations and improve management efficiency with ERP solutions.
Understanding the Dynamics of the Education ERP Market
To fully understand the impact of ERP systems on the market, it’s important to know about the upstream and downstream dynamics involved. When it comes to Education ERP, upstream dynamics refer to the processes and activities that go into creating and supplying ERP software. This includes things like research and development, software design, programming, and testing. On the other hand, downstream dynamics involve how these systems are delivered, implemented, used, and supported within educational institutions.
Who’s Involved in the Education ERP Ecosystem?
There are several key players who have a significant influence on both upstream and downstream dynamics:
- Software Developers: These are the people responsible for designing and building ERP solutions specifically tailored to meet the needs of educational institutions.
- System Integrators: They play a crucial role in helping educational institutions implement ERP systems effectively. Their job is to ensure that these new systems seamlessly integrate with any existing infrastructure already in place.
- Educational Institutions: Ultimately, it is the educational institutions themselves who will be using these ERP solutions. They are considered end-users and their adoption of such technologies is vital for success.
- Government Bodies: Regulations and policies set forth by government bodies can have a significant impact on ERP adoption within education. Depending on whether these regulations are supportive or restrictive, they can either drive or hinder market growth.
- Technology Vendors: In order for an ERP system to be deployed successfully, necessary hardware and support services need to be provided. This is where technology vendors come into play as they supply these resources.
How Do These Dynamics Affect Market Growth?
The interplay between these various stakeholders has a direct influence on the growth of the Education ERP market:
- Advancements in technology driven by software developers lead to more advanced and sophisticated ERP solutions being offered.
- These improved offerings become attractive options for educational institutions looking to streamline their operations.
- System integrators play a crucial role in ensuring that these new solutions are implemented effectively within existing setups.
- Any compatibility issues with legacy systems (older technology still in use) can pose major barriers if not addressed properly.
Government regulations also have a significant impact:
- Supportive policies encourage educational institutions to invest in new technologies like ERPs.
- On the other hand, stringent data privacy laws may require additional compliance measures which could affect implementation timelines.
Ultimately, it is the demand from educational institutions themselves that drives market growth:
- As they seek out advanced solutions that enhance operational efficiency and improve student engagement, this creates opportunities for further expansion within the sector.
The collaboration among all these different stakeholders fosters innovation and adaptability in Education ERPs – leading us closer towards our projected goal of $24.5 billion by 2025!
Key Trends Shaping the Education ERP Industry
Recent developments in technology have significantly influenced the landscape of Education ERP systems. Three primary trends are at the forefront: cloud-based solutions, AI integration, and user experience optimization.
Increasing Adoption of Cloud-Based ERP Systems
Educational institutions are progressively turning to cloud-based ERP solutions for their flexibility and scalability. Unlike traditional on-premises systems, cloud-based ERPs offer seamless access to information from any location, an essential feature in today’s increasingly digital education environment. This ability to access data anywhere ensures continuity in educational processes and supports hybrid learning models.
Cloud solutions also reduce the need for extensive IT infrastructure investment, which is particularly beneficial for institutions facing budget constraints. By adopting these systems, schools and universities can allocate resources more efficiently, focusing on enhancing educational outcomes rather than maintaining legacy systems.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Enhancing Functionality
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing how Education ERPs function by introducing automation and advanced analytics capabilities. AI-driven features such as predictive analytics facilitate better decision-making by providing insights into student performance trends, resource allocation, and administrative efficiencies.
For example, AI algorithms can predict student dropouts by analyzing patterns in attendance and grades, allowing institutions to intervene proactively. Additionally, AI-powered chatbots streamline communication between students and administration, enhancing engagement without increasing human resource demands.
Importance of User Experience in System Design
The success of any ERP system heavily relies on its user experience (UX). A user-friendly interface ensures that both educators and students can navigate complex functionalities effortlessly. Designing systems with intuitive dashboards and accessible features leads to higher adoption rates among users who may be resistant to technological change.
Institutions that prioritize UX in their ERP systems typically see improved satisfaction levels among staff and students alike. This emphasis on design not only facilitates smoother implementation but also maximizes the system’s potential by ensuring all stakeholders can utilize it effectively.
These trends underscore the transformative power of technology within the education sector. Embracing cloud-based solutions, integrating AI capabilities, and prioritizing user experience are essential strategies for educational institutions aiming to enhance operational efficiency and enrich learning environments.
Overcoming Restrictions in Education ERP Adoption and Integration
Adopting an Education ERP system presents several hurdles for educational institutions, often stemming from budget constraints and resistance to change. These barriers can significantly impact the decision-making process and the eventual implementation of new technologies.
Common Barriers to Adoption
1. Budget Constraints
One of the most significant challenges institutions face is limited financial resources. Implementing a comprehensive ERP system can be costly, including initial setup fees, ongoing maintenance, and potential upgrades. This financial burden can be daunting for many schools, particularly smaller institutions with tight budgets.
2. Resistance to Change
Introducing new technology often encounters opposition from staff accustomed to traditional methods. Educators and administrators may fear the complexity of new systems or doubt their ability to learn and integrate them into daily operations.
Technical and Cultural Challenges
Integrating a new ERP system with existing infrastructure involves both technical and cultural hurdles:
1. Technical Challenges
Compatibility issues with legacy systems can complicate integration. Existing infrastructure might not support newer ERP solutions, requiring substantial upgrades or complete overhauls. Data migration also poses risks, as transferring information from outdated systems to modern platforms must be handled meticulously to prevent data loss or corruption.
2. Cultural Challenges
Shifts in organizational culture are often necessary when implementing new technology. An institution’s traditional practices might need reevaluation to accommodate modern workflows facilitated by ERP systems. This shift requires buy-in from all stakeholders to ensure successful integration.
Strategies for Effective Change Management
Implementing strategic change management can help institutions overcome these obstacles:
- Stakeholder Engagement: Early involvement of key stakeholders—including educators, IT personnel, and administrative staff—ensures that their concerns are addressed and their insights are incorporated into the planning process.
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Offering structured training sessions helps ease the transition by equipping staff with the necessary skills to operate new systems effectively. Continuous support post-implementation is also crucial for addressing any emerging issues or questions.
- Phased Implementation Approach: Gradually rolling out ERP components allows institutions to manage changes more effectively. Starting with non-critical modules enables organizations to adjust processes incrementally before tackling more complex areas like finance or human resources.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing channels for ongoing feedback allows for real-time adjustments based on user experiences, fostering a collaborative environment where improvements align closely with institutional needs.
By acknowledging these barriers and implementing tailored strategies, educational institutions can navigate the complexities associated with adopting and integrating Education ERP systems successfully, paving the way for enhanced efficiency and improved outcomes within the education sector.

Geopolitical Factors Impacting Education ERP Software Development
Geopolitical influences play a crucial role in shaping the development of education ERP software across different regions. Trade policies and international relations can significantly impact how software is developed, distributed, and supported globally. For instance, trade agreements or restrictions between countries can determine the availability of certain technologies and resources necessary for ERP development, affecting timelines and costs.
Regulatory Environment
The regulatory environment is another critical factor impacting the implementation and use of Education ERPs. Data privacy laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) in the U.S. set stringent standards for managing student data. Compliance with these regulations is essential for ERP providers to ensure their solutions are legally viable and secure, influencing both design and operational practices.
Global Collaboration
Global collaboration among vendors, educational institutions, and governments becomes imperative for driving innovation in this sector. Collaborative efforts can help overcome geopolitical barriers by encouraging knowledge exchange, sharing best practices, and developing standards that transcend national borders. This cooperation fosters technological advancements that cater to diverse educational needs while ensuring compliance with various regulatory requirements.
By understanding these geopolitical dynamics, stakeholders in the education ERP market can better navigate challenges and leverage opportunities to advance technology adoption worldwide. The balance between adhering to local regulations and embracing global collaboration will continue to shape the future trajectory of education ERP development.
Market Segmentation: Different Types of Education ERP Solutions
Understanding the various types of Education ERP solutions is crucial for comprehending their influence on educational institutions. This market is mainly divided into systems designed for K-12 education and those specifically created for higher education institutions, each with its own unique features and functionalities.
Types of ERPs
1. K-12 Education ERPs
These systems are primarily focused on serving schools from kindergarten to 12th grade.
Features: These systems typically emphasize functionalities like attendance tracking, grade reporting, and communication tools for parents and teachers. They often include modules for managing school operations such as scheduling, student records, and extracurricular activities.
Benefits: By streamlining administrative tasks, K-12 ERPs free up educators to focus more on teaching and less on paperwork.
2. Higher Education ERPs
These are more complex systems designed to cater to the needs of colleges and universities.
Features: These are more complex, often encompassing student information systems, course registration, financial aid management, alumni relations, and more.
Benefits: Higher education ERPs facilitate seamless integration across various departments, ensuring that data flows efficiently between admissions offices, faculty departments, and financial services.
Custom Solutions vs. Off-the-Shelf Products
When it comes to choosing an ERP solution, educational institutions have two main options: custom solutions or off-the-shelf products. Each option has its own advantages and disadvantages.
1. Custom Solutions
These are tailored solutions developed specifically for an institution’s requirements.
Advantages: Tailored to meet the specific needs of an institution, offering unique functionalities that align with particular operational requirements.
Disadvantages: Often more costly and time-consuming to develop. They may require ongoing maintenance from specialized staff.
2. Off-the-Shelf Products
These are standardized solutions available in the market.
Advantages: Cost-effective with quicker deployment times. These standardized solutions come with pre-defined features that cater to general educational needs.
Disadvantages: Lack customization options which might limit their adaptability to unique institutional processes.
Modular vs. Integrated Systems
Another important consideration in the selection process is whether to opt for modular systems or integrated systems.
1. Modular Systems
These are flexible solutions that offer separate modules for different functions.
Flexibility: Offer separate modules for different functions such as student management or finance. Institutions can choose only the modules they require, allowing for a flexible approach to system implementation.
Scalability: Easily scalable as new modules can be added over time to accommodate growing needs.
2. Integrated Systems
These provide a comprehensive suite where all functionalities are built into a single system.
Comprehensive Suite: Provide a complete package where all functionalities are built into a single system. This can lead to better data integration across departments but may sacrifice flexibility.
Limitations: Customization might be limited as changes could affect the entire system’s functionality.
Exploring these types of ERP systems reveals the varied approaches institutions can take based on their specific needs and capacities. Balancing between customization and standardization or choosing between modularity and integration depends largely on institutional goals and resource availability. This nuanced understanding helps stakeholders make informed decisions aligning technology adoption with educational objectives.
Applications of Education ERP Systems in K-12 and Higher Education
Education ERP systems have become essential tools in various educational levels, providing customized features to meet the specific needs of K-12 schools and higher education institutions. These systems simplify complex processes, ensuring smooth information flow and improving operational efficiency.
K-12 Education Applications
In K-12 education, student information systems are crucial. They offer comprehensive solutions for:
- Attendance Tracking: Automated attendance systems reduce manual errors, providing real-time data access for teachers and administrators.
- Grade Reporting: Simplifies the grading process by integrating with classroom management tools, allowing educators to input and manage student grades efficiently.
- Parental Portal Access: Enables parents to monitor their child’s academic progress, attendance records, and school announcements through a centralized platform.
These applications ensure that educators can focus more on teaching while administrative tasks become more manageable.
Higher Education Applications
In higher education institutions, ERP systems transform traditional administrative functions, playing a vital role in:
- Admissions Processes: Streamlines application handling through automated workflows, enhancing the speed and accuracy of processing student applications.
- Course Scheduling: Facilitates efficient management of course offerings by aligning resources with student demand, optimizing classroom utilization.
- Financial Management Software for Schools/Universities: Offers robust tools for budgeting and financial reporting, aiding in strategic planning and resource allocation.
These features not only improve institutional efficiency but also enhance the student experience by reducing administrative bottlenecks.
The increasing adoption of these ERP solutions highlights their critical role in modernizing educational infrastructure. As institutions continue to embrace digital transformation, the demand for sophisticated ERP systems will likely grow within both K-12 and higher education sectors.
Global Insights: Education ERP Market Growth Across Key Regions
Several key trends are reshaping the global landscape for Education ERP solutions. At the forefront are digitalization initiatives led by governments, which are driving educational institutions to adopt advanced ERP systems. This push for digital transformation goes beyond simply upgrading infrastructure; it aims to improve both educational delivery and administrative efficiency.
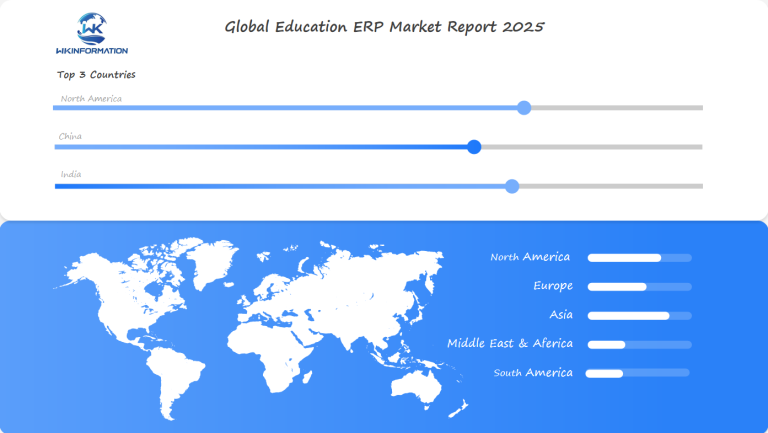
U.S., China, and India: Leading the Charge
In countries such as the U.S., China, and India, these efforts are further intensified by increasing competition among universities and colleges. Institutions are constantly striving to attract students, and offering better services powered by strong ERP systems gives them a significant advantage. By investing in state-of-the-art technology, educational institutions can optimize their operations, engage students more effectively, and enhance their overall performance.
Here’s how each region is approaching Education ERP:
- In the U.S., the emphasis is often on implementing comprehensive ERP solutions that cater to various administrative requirements.
- China is utilizing its technological advancements to deploy cutting-edge ERP systems designed for large-scale educational settings.
- India is witnessing a growing market where infrastructure development and government support are pushing the limits of technology integration in education.
This combination of global market trends not only increases the demand for Education ERPs but also creates opportunities for ongoing innovation and growth in this industry.
The USA’s Impact on Education ERP Innovation and Adoption
The United States is leading the way in Education ERP innovation, significantly influencing global trends. With its advanced technology infrastructure and investment in educational technologies, the U.S. has become a frontrunner in adopting state-of-the-art ERP solutions.
1. Investment in Technology
American educational institutions are heavily investing in ERP systems to address various operational challenges. From managing student information and financial operations to human resources, these systems offer comprehensive solutions that streamline processes across campuses.
2. Innovation Hubs
Silicon Valley and other tech hubs are breeding grounds for startups and established companies developing innovative ERP solutions tailored to education. These innovations often incorporate Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, enhancing the capabilities of traditional ERPs.
3. Government Support
Federal and state-level policies support digital transformation in education, encouraging institutions to adopt advanced technologies. Grants and funding initiatives make it easier for schools to implement these systems, increasing adoption rates.
4. Focus on User Experience
American ERPs emphasize user-friendly interfaces, ensuring that educators and administrators can easily navigate complex systems. This focus leads to higher adoption rates and more efficient use of technology.
The U.S.’s proactive approach not only enhances the educational landscape domestically but also influences international markets seeking to emulate American success in educational technology integration.
China’s Role in Advancing Education ERP Solutions in Schools and Universities
China is leading the way in adopting Education ERP solutions, making significant progress in both schools and universities. The Chinese government’s emphasis on educational reform and technological innovation has created an environment conducive to the widespread use of digital solutions in education.
1. Government Initiatives
China’s government actively promotes smart education, integrating technology into classrooms to enhance learning. This includes substantial investments in developing robust ERP systems that support educational administration and management.
2. Localized Customization
With a diverse educational landscape, China’s ERP solutions are often tailored to meet specific regional needs. Local vendors collaborate with educational institutions to create systems that align with China’s unique educational policies and practices.
3. Integration with AI
Chinese ERPs increasingly incorporate AI capabilities, offering features like predictive analytics for student performance, automated administrative tasks, and personalized learning pathways. These innovations help streamline operations and provide data-driven insights for better decision-making.
4. Impact on Higher Education
Universities in China leverage advanced ERP systems to manage complex functions such as research administration, faculty management, and international collaborations. This technological edge enhances operational efficiency and global competitiveness.
China’s proactive approach in developing comprehensive ERP solutions not only supports its domestic education sector but also serves as a model for other countries seeking to modernize their educational infrastructure.
India’s Expanding Education ERP Market and Infrastructure Development
India’s education sector is undergoing a transformational journey, driven by the rapid adoption of Education ERP systems. A key factor contributing to this growth is the government’s commitment to enhancing digital infrastructure across educational institutions. Initiatives like the Digital India campaign are crucial in integrating technology into classrooms and administration.
Key Drivers of Growth:
- Government Initiatives: Policies aimed at modernizing educational facilities emphasize ERP solutions as integral to improving operational efficiency.
- Increased Investment: Both public and private sectors are channeling substantial resources into ERP technology, recognizing its potential to streamline processes such as student admissions, fee management, and faculty coordination.
- Customization Needs: With India’s diverse educational landscape, there is a significant demand for customizable ERP solutions tailored to meet specific institutional requirements.
Impact on Educational Institutions:
Educational institutions across India are leveraging ERP systems to enhance their administrative capabilities. Universities and colleges utilize these platforms for effective management of academic records and financial operations. Schools benefit from improved communication channels with parents and students, fostering a more integrated learning environment.
As India’s infrastructure continues to develop, the role of Education ERP systems becomes even more crucial in supporting an efficient, technology-driven educational framework. This growing market reflects a broader trend of digital transformation across the region, underscoring the importance of robust technological solutions in shaping the future of education.
Future Innovations in Education ERP Technologies
The education sector is on the brink of significant technological advancements as ERP systems evolve to meet growing demands. Several innovations are anticipated to reshape the landscape of Education ERPs:
1. AI-Enhanced Predictive Analytics
Artificial Intelligence will play a central role, offering predictive analytics capabilities that can forecast student performance, optimize resource allocation, and personalize learning experiences. AI can analyze vast datasets to provide insights that were previously inaccessible.
2. Blockchain for Data Security
As data privacy concerns rise, blockchain technology presents a promising solution for securing educational records. This decentralized ledger system ensures data integrity and enhances trust between stakeholders by preventing unauthorized access and data tampering.
3. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
IoT devices are expected to integrate with ERP systems to enhance real-time monitoring and management of campus facilities. From smart classrooms to automated attendance systems, IoT can facilitate seamless communication between physical infrastructure and digital platforms.
4. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
These immersive technologies offer new possibilities for interactive learning environments. Education ERPs could incorporate AR/VR to develop virtual labs or simulation-based training modules, enhancing experiential learning opportunities.
These innovations promise to deliver more intuitive, efficient, and secure ERP solutions tailored to the unique needs of educational institutions worldwide, paving the way for a technologically advanced future in education management.
Leading Competitors in the Education ERP Market
The Education ERP market is populated by several key players:
- SAP
- Oracle
- Blackbaud
- Ellucian
- Unit4
- Microsoft
- Sage
- Infor
- Jenzabar
- Workday
Overall
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Global Education ERP Market Market Report |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Segment by Type |
· On-Premise · Cloud-Based |
| Segment by Application |
· K-12 Education Applications · Higher Education Applications |
| Geographies Covered |
· North America (United States, Canada) · Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Russia) · Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan) · Southeast Asia (India) · Latin America (Mexico, Brazil) |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
The Education ERP market is growing rapidly and is expected to reach $24.5 billion by 2025. This growth is mainly driven by digital transformation efforts in the U.S., China, and India, where educational institutions are increasingly adopting advanced technologies.
Key trends driving this expansion include:
- Cloud-Based Solutions: These enable seamless access to educational resources, simplify data management, and enhance operational efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI is revolutionizing education by making ERP systems more intuitive and efficient, streamlining processes from admissions to financial management.
Educational institutions face challenges in ERP adoption, such as budget constraints and integration difficulties. However, strategic change management can mitigate these barriers, ensuring a smooth transition to new systems.
Geopolitical factors, like trade policies and data privacy laws, impact ERP software development and implementation. Global collaboration among vendors and educational bodies is crucial for fostering innovation and technological advancement.
Different types of ERPs cater to diverse educational needs, offering solutions tailored for K-12 schools as well as higher education institutions. These systems play a vital role in improving institutional efficiency through applications like attendance tracking and course scheduling.
The demand for sophisticated ERP solutions continues to grow globally, reflecting the ongoing convergence of technology with education. This transformation is reshaping how institutions operate and engage with students, setting the stage for future innovations in education ERP technologies.
Global Education ERP Market Report (Can Read by Free sample) – Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Education ERP Market Analysis Overview
- Competitive Forces Analysis (Porter’s Five Forces)
- Strategic Growth Assessment (Ansoff Matrix)
- Industry Value Chain Insights
- Regional Trends and Key Market Drivers
- Education ERPMarket Segmentation Overview
Chapter 2: Competitive Landscape
- Global Education ERP players and Regional Insights
- Key Players and Market Share Analysis
- Sales Trends of Leading Companies
- Year-on-Year Performance Insights
- Competitive Strategies and Market Positioning
- Key Differentiators and Strategic Moves
Chapter 3: Education ERP Market Segmentation Analysis
- Key Data and Visual Insights
- Trends, Growth Rates, and Drivers
- Segment Dynamics and Insights
- Detailed Market Analysis by Segment
Chapter 4: Regional Market Performance
- Consumer Trends by Region
- Historical Data and Growth Forecasts
- Regional Growth Factors
- Economic, Demographic, and Technological Impacts
- Challenges and Opportunities in Key Regions
- Regional Trends and Market Shifts
- Key Cities and High-Demand Areas
Chapter 5: Education ERP Emerging and Untapped Markets
- Growth Potential in Secondary Regions
- Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
Chapter 6: Product and Application Segmentation
- Product Types and Innovation Trends
- Application-Based Market Insights
Chapter 7: Education ERP Consumer Insights
- Demographics and Buying Behaviors
- Target Audience Profiles
Chapter 8: Key Findings and Recommendations
- Summary ofEducation ERP Market Insights
- Actionable Recommendations for Stakeholders
Access the study in MULTIPLEFORMATS
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1-866-739-3133
Email: infor@wkinformation.com
What is the projected growth of the Education ERP market by 2025?
The Education ERP market is projected to expand to $24.5 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions and AI integration.
What are the key dynamics influencing the Education ERP market?
The key dynamics include upstream and downstream influences, where stakeholders play significant roles in shaping the market’s growth through their interactions and contributions within the Education ERP ecosystem.
What trends are currently shaping the Education ERP industry?
Key trends include the increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions, integration of Artificial Intelligence for enhanced functionality, and a focus on user experience to improve system design and utilization.
What challenges do educational institutions face when adopting Education ERP systems?
Common barriers include budget constraints, resistance to change, technical integration challenges with existing infrastructure, and cultural issues that can hinder effective change management.
How do geopolitical factors affect the development of Education ERP software?
Geopolitical influences such as trade policies and international relations impact software development processes, while regulations like data privacy laws shape how Education ERPs are implemented and used globally.
What types of Education ERP solutions are available in the market?
There are various types of Education ERPs including those designed for K-12 versus higher education institutions. They can be categorized into custom solutions tailored to specific needs or off-the-shelf products, as well as modular systems offering flexibility versus fully integrated


