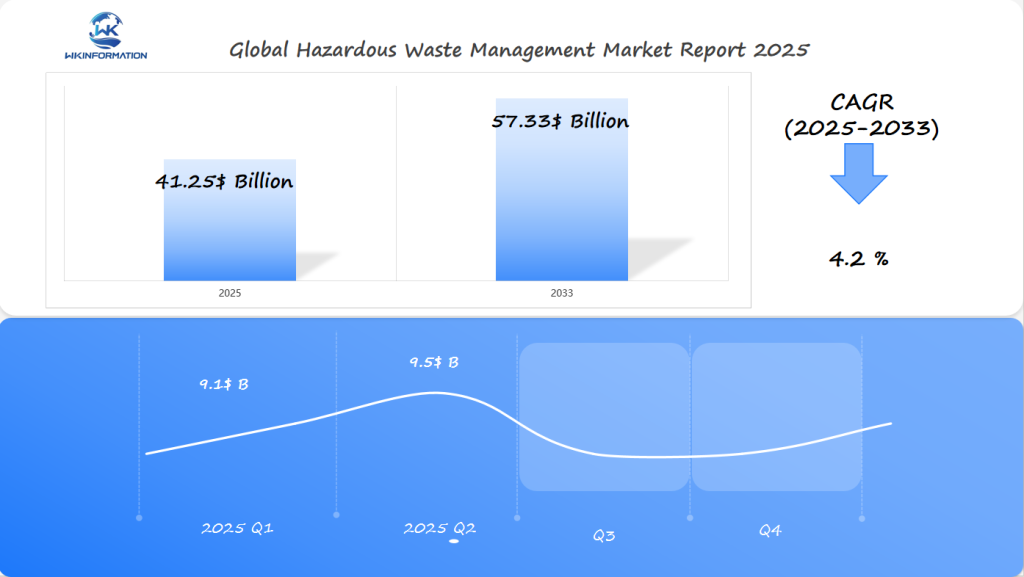
2025 Hazardous Waste Management Market Growth: Reaching $41.25 Billion with Increasing Environmental Regulations in USA, India, and Australia
Discover how the hazardous waste management market in the US, India, and Australia will evolve by 2025, influenced by Trump-era policies and sustainability initiatives. Learn about market growth projections, regulatory changes, and key industry challenges.
- Last Updated:
Hazardous Waste Management Market: Q1 and Q2 2025 Predictions
The global Hazardous Waste Management market is projected to reach USD 41.25 billion in 2025, driven by increasing industrial activities and stringent environmental regulations. With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.20% through 2033, the market is expected to expand steadily.
In Q1 2025, the market is likely to generate around USD 9.1 billion, which represents approximately 22% of the annual market value. This early growth is driven by heightened regulatory scrutiny and the growing volume of industrial waste in key regions, particularly in the U.S., India, and Australia, where economic growth is accompanied by an increase in waste generation. By Q2 2025, the market is expected to grow to about USD 9.5 billion, as governments and industries in these countries invest in sustainable waste management technologies to meet stricter environmental standards.
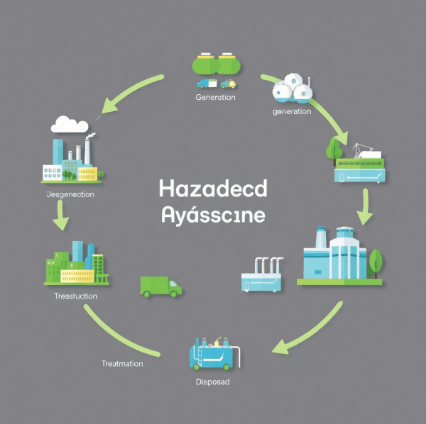
Understanding Upstream and Downstream Processes in Hazardous Waste Management
Understanding the upstream and downstream processes in hazardous waste management is crucial for optimizing efficiency and ensuring regulatory compliance. These processes define the entire lifecycle of hazardous waste, from its initial generation to its ultimate disposal.
Upstream Processes
- Generation: The beginning of the hazardous waste lifecycle occurs at industrial facilities, healthcare centers, and various other sectors where waste is produced. This stage involves identifying and classifying waste types based on their potential environmental impacts.
- Collection and Segregation: Proper collection practices are essential to prevent contamination. Segregating waste into categories such as chemical, biomedical, or radioactive helps in determining suitable treatment methods later.
Downstream Processes
- Transportation: Once collected, the safe transport of hazardous waste to treatment facilities is vital. This involves adhering to strict regulations concerning packaging and labeling to prevent accidents during transit.
- Treatment and Disposal: At this stage, waste undergoes treatment using methods like incineration or chemical processing. The goal is to neutralize harmful effects before final disposal in landfills or through recycling.
Integration for Efficiency
Integrating upstream and downstream activities ensures seamless transitions between stages, reducing risks of mishandling or environmental contamination. A coordinated approach improves resource allocation, enhances safety protocols, and aligns with stringent regulatory requirements.
The dynamic interplay between these processes emphasizes the need for holistic management strategies in today’s environmentally-conscious world. By focusing on both ends of the hazardous waste lifecycle, businesses can achieve sustainable operations while contributing positively to public health and ecological preservation.
Key Trends Shaping the Hazardous Waste Management Industry
The hazardous waste management industry is experiencing significant changes due to various factors. These changes are being driven by urgent environmental issues and advancements in technology.
1. Digital Transformation
The industry is undergoing a digital transformation, with the adoption of smart technologies that enable real-time monitoring and data analytics. This shift towards digital solutions is improving operational efficiency and helping businesses comply with strict regulations.
2. Embracing Circular Economy Principles
More and more companies are embracing circular economy principles, which focus on resource recovery and recycling initiatives. By integrating these principles into their operations, industries can reduce waste generation and minimize their impact on the environment.
3. Role of Innovations
Innovations are crucial in advancing hazardous waste management. New treatment technologies like plasma gasification and bioremediation offer more sustainable alternatives for waste disposal. Additionally, waste-to-energy solutions are becoming increasingly important as they convert waste into valuable energy resources while reducing reliance on landfills.
4. Importance of Strategic Collaborations
Strategic collaborations among companies are essential for driving growth in the industry. Partnerships between technology providers and waste management firms enable the development of innovative solutions that cater to specific needs. These alliances also promote knowledge sharing and capacity building, ultimately enhancing market competitiveness.
5. Leading Players in the Industry
Key players such as Veolia and Suez Group are at the forefront of this industry transformation. They are making significant investments in cutting-edge technologies and forming strategic alliances to strengthen their position in the market.
These emerging trends indicate a dynamic industry that is expected to experience substantial growth due to innovation and collaboration.
Overcoming Regulatory Restrictions and Challenges in Hazardous Waste Management
Navigating the regulatory frameworks that govern hazardous waste management is a complex but crucial task for companies in this sector. These frameworks are designed to ensure that hazardous waste is managed in a manner that protects both public health and the environment.
Overview of Global Regulatory Frameworks
Here’s a brief overview of some key global regulatory frameworks governing hazardous waste management:
- United States: The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) provides the foundation for waste management regulations, focusing on reducing hazardous waste generation and promoting safe disposal.
- Europe: The European Union’s Waste Framework Directive emphasizes waste hierarchy principles, aiming to prevent waste and encourage recycling.
- Asia-Pacific: Countries like India are increasingly adopting stringent regulations similar to Western standards, driven by rapid industrialization.
Key Compliance Challenges
Companies face several hurdles while trying to comply with these regulations:
- Varying Standards: Different countries have distinct regulatory standards, making it challenging for multinational companies to maintain consistent compliance.
- Cost Implications: Implementing necessary changes to meet regulatory requirements often involves significant financial investment.
- Technological Limitations: In some regions, outdated technology hinders companies’ ability to comply with modern standards.
Strategies for Overcoming Regulatory Obstacles
To address these challenges, companies can adopt several strategies:
- Proactive Planning: Anticipating regulatory changes allows companies to prepare in advance, minimizing disruptions.
- Collaboration with Authorities: Engaging in dialogue with regulatory bodies can offer insights into compliance requirements and potential upcoming changes.
- Investing in Technology: Upgrading technology not only enhances compliance but also boosts operational efficiency.
By understanding these frameworks and challenges, companies can better position themselves within the growing Hazardous Waste Management Market.
The Geopolitical Impact on Hazardous Waste Disposal and Recycling Strategies
Geopolitical factors play a crucial role in shaping hazardous waste disposal strategies. The international trade of hazardous waste materials is heavily influenced by political relationships, trade agreements, and regulatory alignments between countries. Geopolitical dynamics can either facilitate or hinder the flow of waste materials across borders, impacting both disposal and recycling practices.
Trade Restrictions and Agreements
Countries with strong trade agreements may find it easier to export and import hazardous waste for treatment, whereas geopolitical tensions can lead to restrictive measures, complicating cross-border waste management efforts.
Infrastructure Development
The development of waste management infrastructure varies greatly between regions, often dictated by economic stability and government priorities. In areas where infrastructure is lacking, geopolitical alliances can provide much-needed investment or technology transfer to enhance local capabilities.
Case Studies
European Union (EU) Harmonization: Within the EU, standardized regulations and cooperative policies enable efficient hazardous waste management across member states. This geopolitical alignment ensures consistent recycling practices and supports circular economy initiatives.
US-China Trade Tensions: The trade war between the US and China resulted in increased tariffs on waste exports, disrupting recycling operations that previously relied on Chinese processing facilities.
These examples show how geopolitics can determine the effectiveness of hazardous waste strategies. The strategic collaborations or disputes between nations not only affect operational efficiencies but also influence global environmental outcomes. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for stakeholders aiming to navigate the complex landscape of international hazardous waste management.
Market Segmentation: Different Types of Hazardous Waste and Their Management Solutions
Understanding the types of hazardous waste is crucial for effective management and disposal. These wastes, generated by both industries and households, come in various forms, each demanding specific handling strategies to mitigate environmental risks.
1. Types of Hazardous Waste:
a. Solid Waste
Often originates from industrial processes or household activities. It includes contaminated materials like batteries, chemical solvents, and electronic waste. Solid waste management typically involves techniques such as landfilling with liners and leachate collection systems to prevent soil contamination.
b. Liquid Waste
Generated largely by industries through processes like chemical manufacturing and oil refining. This category demands careful treatment methods, such as chemical neutralization or biological treatment, to reduce toxicity before disposal.
c. Sludge
A semi-solid byproduct from wastewater treatment plants or industrial processes. Its management often involves dewatering to reduce volume followed by safe disposal or incineration.
2. Specific Categories Requiring Tailored Solutions:
a. Chemical Waste
Includes substances such as acids, alkalis, and reactive compounds. Requires specialized containment and neutralization processes to prevent hazardous reactions during storage and transportation.
b. Biomedical Waste
Produced in healthcare facilities, it encompasses sharps, pathological waste, and pharmaceuticals. Effective sterilization methods like autoclaving are essential to minimize public health risks.
c. Radioactive Waste
Originating from nuclear power plants or medical treatments, this type demands stringent protocols for containment and long-term storage in designated facilities to prevent radiation exposure.
Each type of hazardous waste requires a unique approach tailored to its characteristics. Proper categorization and management solutions are vital in ensuring safety and compliance with regulatory frameworks. This understanding not only aids in protecting the environment but also supports sustainable industry practices.
Applications of Hazardous Waste Management in Industries and Environmental Protection
Effective hazardous waste management is crucial in reducing environmental impacts caused by industrial activities. These activities often produce large amounts of hazardous waste, which can harm the environment if not handled properly. By adopting efficient waste management practices, industries can greatly decrease their negative impact on nature.
Minimizing Environmental Impacts:
- Waste Segregation and Treatment: Properly separating and treating hazardous waste prevents harmful substances from entering the environment. Methods such as incineration and chemical treatment are used to neutralize toxic components.
- Resource Recovery: Following circular economy principles allows for the recovery and recycling of valuable materials from waste streams, reducing the need for raw material extraction and minimizing environmental stress.
Protecting Public Health:
Hazardous waste management is essential in protecting public health. Improperly managed hazardous waste can expose communities to serious health risks, including respiratory issues, skin conditions, and long-term illnesses. Effective management practices involve:
- Safe Disposal Methods: Using secure landfill sites or advanced treatment facilities ensures that contaminants are isolated from populated areas.
- Strict Compliance with Regulations: Following strict regulatory frameworks helps prevent illegal dumping and keeps communities safe from exposure to toxic substances.
Industrial Responsibility:
Industries are increasingly acknowledging their duty towards both environmental protection and public health. By investing in advanced hazardous waste management solutions, companies not only meet regulations but also contribute to sustainable development goals.
The integration of innovative technologies like AI-driven monitoring systems further enhances the effectiveness of waste management efforts, ensuring that industrial operations remain sustainable and environmentally conscious.
Regional Growth Insights: Hazardous Waste Management Market Across Different Regions
Asia-Pacific: Leading the Way
The Asia-Pacific region stands out in the hazardous waste management market, largely due to its rapid industrialization and urbanization. Countries like China and India are experiencing significant growth driven by increasing manufacturing activities and stringent environmental regulations. This expansion is supported by substantial investments in infrastructure development to manage waste effectively.
Key Players in Asia-Pacific
- China: As one of the world’s largest producers of industrial waste, China has been investing heavily in advanced waste treatment technologies. The government’s focus on sustainability and pollution control presents opportunities for further market growth.
- India: Emerging as a pivotal player in the regional market, India is actively enhancing its waste management infrastructure. Initiatives such as the Swachh Bharat Mission aim to improve waste collection and processing systems across urban areas.
North America: Sustaining Revenue Share
The North American market, particularly in the United States, continues to hold a significant revenue share due to its robust healthcare system and substantial governmental support for recycling initiatives. The emphasis on sustainable practices and technological advancements positions North America as a leader in hazardous waste management solutions.
Africa: Overcoming Challenges
In contrast, regions like Africa face challenges due to limited infrastructure and lack of regulatory enforcement. However, international partnerships and foreign investments are gradually improving waste management capabilities.
Future Projections
Future projections highlight the potential for continued growth across emerging economies. The integration of digital technologies and strategic collaborations between private and public sectors will be critical in shaping the future landscape of hazardous waste management globally. With ongoing industrial expansion and urban development, these markets are expected to play an increasingly vital role in driving industry advancements.
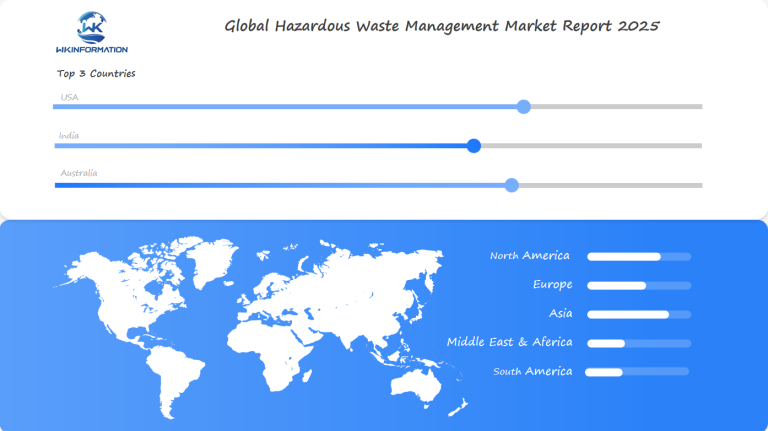
The USA’s Leading Role in Hazardous Waste Management Solutions
The United States is a leader in managing hazardous waste, with its strong infrastructure and regulations setting an example for others around the world. This leadership is based on several important factors:
1. Regulatory Frameworks
The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) plays a crucial role in regulating hazardous waste from its creation to disposal, ensuring comprehensive oversight. This legislation has been instrumental in driving compliance and innovation within the industry.
2. Technological Innovations
American companies are leading the way with new technologies such as bioremediation, which uses natural organisms to clean up polluted areas, and thermal desorption for removing harmful substances using heat.
3. Public-Private Partnerships
Collaboration between government agencies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and private companies creates an environment that encourages research and development. These partnerships provide funding for cutting-edge projects that improve waste treatment effectiveness.
4. Waste-to-Energy Initiatives
The USA is at the forefront of turning waste into energy, reducing the need for landfills while producing renewable energy. Facilities across the country use this process to sustainably power communities.
These factors highlight the USA’s dedication to protecting the environment and finding innovative solutions for hazardous waste management. This pioneering approach not only tackles domestic issues but also sets a global standard that shapes international policies and practices.
India’s Expanding Hazardous Waste Management Infrastructure
India’s hazardous waste management infrastructure is witnessing remarkable growth, driven by rapid industrialization and urbanization. The country faces increasing pressure to manage its hazardous waste effectively due to the rising volume generated by various industries.
Key Drivers of Infrastructure Expansion
1. Industrial Growth
With a booming industrial sector, India is seeing a surge in hazardous waste production. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and electronics are major contributors.
2. Government Initiatives
Indian government policies play a crucial role in expanding waste management facilities. Initiatives like the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan emphasize sustainable waste management practices.
3. Public Awareness
Rising awareness about environmental health risks associated with improper disposal of hazardous waste is pushing for better infrastructure.
Strategic Developments
Efforts to enhance hazardous waste management include:
- Advanced Treatment Technologies: Adoption of modern technologies like incineration and chemical treatment to safely process hazardous materials.
- Private Sector Involvement: Increased participation from private players in waste collection and treatment services contributes to infrastructure development.
- Regional Focus: States like Maharashtra and Gujarat lead in establishing comprehensive management systems, setting examples for other regions.
India’s proactive approach towards improving its hazardous waste management infrastructure showcases a commitment to environmental sustainability and public health protection. This growth presents opportunities for both local and international stakeholders to invest in innovative solutions tailored to India’s unique challenges.
Australia’s Commitment to Sustainable Hazardous Waste Disposal
Australia is a leader in sustainable hazardous waste management, prioritizing environmental conservation and public health. The country has implemented strict regulations and policies to ensure the safe disposal and treatment of hazardous waste, demonstrating its commitment to minimizing ecological impact.
1. Regulatory Framework
Australia’s regulatory landscape includes comprehensive legislation such as the National Waste Policy and the Hazardous Waste (Regulation of Exports and Imports) Act 1989. These frameworks guide the safe handling, transportation, and disposal of hazardous materials, ensuring compliance with international standards.
2. Innovative Approaches
Emphasizing innovation, Australia invests in advanced waste treatment technologies. Facilities across the country are increasingly adopting methods like thermal desorption and plasma gasification, enhancing waste reduction efficiencies while reducing harmful emissions.
3. Public-Private Partnerships
Collaboration between government bodies and private enterprises plays a pivotal role. Initiatives such as the Australian Packaging Covenant demonstrate effective partnerships that promote sustainable practices across industries.
4. Community Engagement
Education programs aim to raise awareness about proper hazardous waste handling among communities, fostering a culture of responsibility towards waste management.
Australia’s proactive approach highlights the importance of integrating cutting-edge technology with robust policy frameworks, setting an example for other nations striving for sustainability in hazardous waste management.
Innovations in Hazardous Waste Management Technologies and Future Trends
The hazardous waste management industry is going through a technological revival, with advancements in technology leading the way. One of the most significant changes is the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in monitoring systems, which has proven to be a game-changer. AI-powered solutions offer improved capabilities for tracking waste materials in real-time, allowing for accurate identification and classification. This, in turn, leads to better waste segregation, which is essential for effective management.
Key Innovations Shaping Hazardous Waste Management
Several key innovations are reshaping the hazardous waste management landscape:
- Automation: Operational procedures at treatment facilities are being transformed by automation. Automated systems streamline tasks such as sorting and handling, significantly reducing human error and increasing processing speed. This results in more efficient operations that minimize environmental impact while maximizing resource recovery.
- Smart Sensors: The implementation of smart sensors within waste management infrastructure is another exciting development. These sensors provide valuable data on waste composition and volume, aiding in predictive maintenance of equipment and facilities. By anticipating potential issues before they occur, companies can avoid costly downtime and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
- Waste-to-Energy Technologies: Sustainable alternatives to traditional disposal methods are gaining popularity, particularly waste-to-energy technologies. These processes convert hazardous waste into usable energy, offering an environmentally friendly solution that reduces reliance on landfills and recycles valuable resources.
- Blockchain Technology: Transparency and traceability in hazardous waste transactions are being enhanced through the use of blockchain technology. By providing a secure ledger of waste movements, blockchain ensures accountability throughout the entire lifecycle of hazardous materials.
Promising Future Ahead
These innovations indicate a promising future for the hazardous waste management sector. Continuous improvements are expected to tackle existing challenges while paving the way for sustainable growth.
As these technologies develop further, they will play a crucial role in supporting global efforts towards more efficient and environmentally-friendly waste management practices.
Major Competitors in the Hazardous Waste Management Market
In the hazardous waste management market, several key players dominate with their innovative solutions and strategic approaches.
- Veolia – France
- Biffa – United Kingdom
- Covanta Holding – United States
- Clean Harbors – United States
- Suez Group – France
- Waste Management – United States
- Stericycle Inc. – United States
- Republic Services Inc. – United States
- Remondis AG – Germany
- Bechtel Corporation – United States
Overall
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Global Hazardous Waste Management Market Market Report |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Segment by Type |
· Solid · Liquid · Sludge |
| Segment by Application |
· Industrial · Commercial · Municipal · Healthcare · Agricultural |
| Geographies Covered |
· North America (United States, Canada) · Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Russia) · Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan) · Southeast Asia (India) · Latin America (Mexico, Brazil) |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
The hazardous waste management market is expected to grow significantly due to a combination of government regulations and technological advancements. As industries expand globally, the need for effective waste management solutions increases, creating a competitive environment full of opportunities.
Key Drivers
- Regulatory Compliance: Increasing environmental regulations necessitate advanced management strategies.
- Technological Innovations: AI integration and automation are set to revolutionize monitoring and operational efficiency.
Emerging economies like India play a crucial role in driving regional growth, while North America continues to lead due to its strong infrastructure and investment landscape. With key players such as Veolia and Suez Group setting benchmarks in the industry, the future outlook promises enhanced sustainability and profitability across the sector.
Global Hazardous Waste Management Market Report (Can Read by Free sample) – Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Hazardous Waste Management Market Analysis Overview
- Competitive Forces Analysis (Porter’s Five Forces)
- Strategic Growth Assessment (Ansoff Matrix)
- Industry Value Chain Insights
- Regional Trends and Key Market Drivers
- Hazardous Waste Management Market Segmentation Overview
Chapter 2: Competitive Landscape
- Global Hazardous Waste Management players and Regional Insights
- Key Players and Market Share Analysis
- Sales Trends of Leading Companies
- Year-on-Year Performance Insights
- Competitive Strategies and Market Positioning
- Key Differentiators and Strategic Moves
Chapter 3: Hazardous Waste Management Market Segmentation Analysis
- Key Data and Visual Insights
- Trends, Growth Rates, and Drivers
- Segment Dynamics and Insights
- Detailed Market Analysis by Segment
Chapter 4: Regional Market Performance
- Consumer Trends by Region
- Historical Data and Growth Forecasts
- Regional Growth Factors
- Economic, Demographic, and Technological Impacts
- Challenges and Opportunities in Key Regions
- Regional Trends and Market Shifts
- Key Cities and High-Demand Areas
Chapter 5: Hazardous Waste Management Emerging and Untapped Markets
- Growth Potential in Secondary Regions
- Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
Chapter 6: Product and Application Segmentation
- Product Types and Innovation Trends
- Application-Based Market Insights
Chapter 7: Hazardous Waste Management Consumer Insights
- Demographics and Buying Behaviors
- Target Audience Profiles
Chapter 8: Key Findings and Recommendations
- Summary ofHazardous Waste Management Market Insights
- Actionable Recommendations for Stakeholders
Access the study in MULTIPLEFORMATS
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1-866-739-3133
Email: infor@wkinformation.com
What are the upstream and downstream processes in hazardous waste management?
In hazardous waste management, upstream processes refer to activities involved in the generation of hazardous waste, including production and initial handling. Downstream processes encompass the treatment, disposal, and recycling of this waste. Understanding these chains is crucial for optimizing the hazardous waste lifecycle and ensuring compliance with regulations.
What key trends are currently shaping the hazardous waste management industry?
Emerging trends in the hazardous waste management industry include digitalization, which enhances data tracking and operational efficiency, and principles of the circular economy that promote waste reduction and resource recovery. Innovations such as advanced treatment technologies and waste-to-energy solutions are also driving sustainability in the sector.
What regulatory challenges do companies face in hazardous waste management?
Companies often encounter various regulatory frameworks that dictate hazardous waste management practices. Key challenges include differing compliance requirements across regions, which can complicate operations. Strategies to overcome these obstacles involve proactive planning, staying informed about regulations, and collaborating with local authorities.
How do geopolitical factors influence hazardous waste disposal strategies?
Geopolitical dynamics significantly impact international trade practices related to hazardous waste materials. Variations in infrastructure development across regions affect recycling practices, leading to different approaches in managing hazardous waste. Case studies illustrate how countries adapt their strategies based on geopolitical considerations.
What types of hazardous waste require specialized management solutions?
Hazardous waste can be categorized into several types including solid, liquid, and sludge. Specific categories like chemical, biomedical, and radioactive wastes have unique characteristics that necessitate tailored management solutions to ensure safe handling and disposal.
How does effective hazardous waste management benefit industries and environmental protection?
Effective hazardous waste management is vital for minimizing environmental impacts from industrial activities. It plays a crucial role in protecting public health by ensuring proper handling and disposal methods are implemented to mitigate risks associated with hazardous materials.

