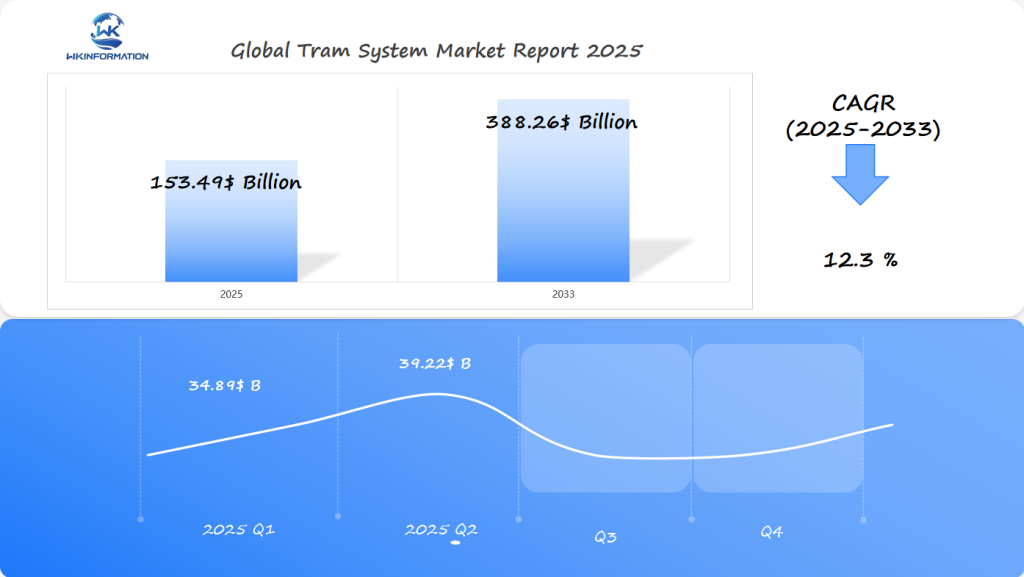
$153.49 Billion Tram System Market Set to Expand in Germany, Australia, and U.S. by 2025
Global Tram System Market poised for substantial growth as urban mobility demands rise, with Germany, Australia, and U.S. leading expansion through innovative transit solutions
- Last Updated:
Projected Market Insights for Tram System in Q1 and Q2 of 2025
The Tram System market is expected to reach $153.49 billion in 2025, growing at a rate of 12.3% per year from 2025 to 2033. In the first quarter, the market is projected to generate around $34.89 billion, driven by increasing investments in sustainable urban transportation and expanding tram networks worldwide. By the second quarter, the market is expected to grow to about $39.22 billion, as cities focus on reducing traffic congestion and carbon emissions.
Key Markets for Tram Systems
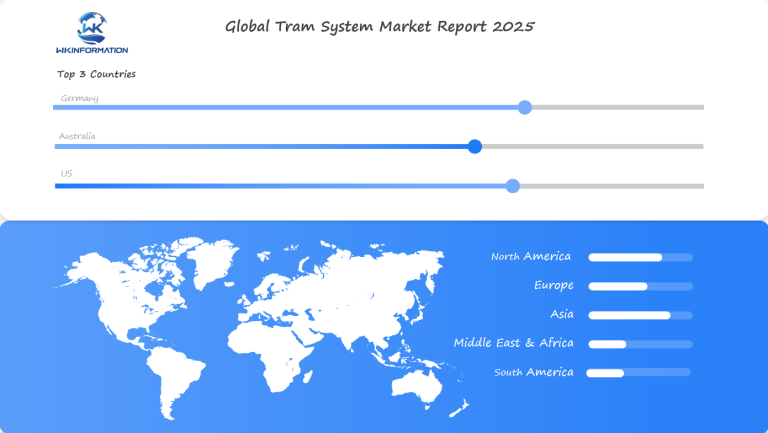
Germany, Australia, and the U.S. are expected to be the main markets for tram systems:
- Germany leads in advanced tram technology and efficient public transport policies.
- Australia is investing heavily in modernizing its urban transit systems.
- The U.S. sees renewed interest in light rail projects in major metropolitan areas.
With rising environmental awareness and government support for public transit infrastructure, tram systems will continue to play a crucial role in future urban mobility solutions.
Understanding the Upstream and Downstream Industry Chains for Tram Systems
The tram manufacturing industry is a complex world of innovation and technology. Big names like Alstom, Siemens Mobility, and CRRC lead in creating new transportation solutions. These solutions change how we move around cities.
Building trams involves complex supply chains and partnerships. These partnerships drive the growth of new technologies. The industry chain includes many important parts and tech areas.
Key Components and Suppliers in Tram Manufacturing
Tram manufacturing involves complex components that require specialized suppliers:
- Advanced electrical systems
- Innovative propulsion technologies
- Lightweight body structures
- High-performance chassis designs
These components are crucial for ensuring the efficiency, safety, and durability of trams. Manufacturers collaborate with specific suppliers who have expertise in producing these parts to maintain high-quality standards.
The success of infrastructure development projects, such as building tram networks, heavily depends on these intricate manufacturing processes.
Infrastructure Development and Maintenance Services
For trams to operate efficiently, a robust infrastructure plan is essential. This plan encompasses:
- Track laying and rail infrastructure
- Electrification network installation
- Station and depot construction
- Integrated urban transit planning
Ensuring the seamless operation of trams is crucial. Expert teams conduct routine inspections to ensure everything runs smoothly, preventing extended service disruptions.
Key Trends Driving the Growth of Tram Systems in Urban Mobility
Urban transportation is changing fast. Tram systems are becoming key for making cities better. They help solve big problems in city life.
Electric transport is changing cities. It’s making public transit better. Cities are choosing electric trams to cut down on pollution and offer better travel options.
Electrification and Sustainable Transportation Solutions
Electric monorails are leading the way in city travel. By 2025, they will make up 71.8% of the market. They offer big benefits like:
- Less carbon emissions
- Lower costs to run
- More energy use
- Quieter rides
Integration with Smart City Initiatives
Tram systems are becoming more advanced by incorporating new technology for improved tracking and maintenance. This leads to a smoother and more efficient travel experience.
Electric tram systems represent the future of sustainable urban transportation, combining technological innovation with environmental responsibility.
Cities are now combining electric transport with smart technology to create better public transportation options that cater to the needs of modern city residents.
Challenges in Developing and Modernizing Tram Infrastructure
Building tram systems is tough for cities around the world. They face big hurdles when they try to grow or update their tram networks. Money and technical issues are the main problems.
Starting a tram project is full of big challenges. These can slow down or stop the creation of efficient tram systems.
Financial Constraints and Funding Models
Getting money is a big worry for city transit planners. The cost to start tram projects is very high. This puts a lot of pressure on city budgets.
- Initial capital costs can exceed $20-50 million per kilometer of track
- Long-term financing requires complex funding strategies
- Public-private partnerships emerging as innovative funding solutions
Technical and Operational Hurdles
There are many technical and practical problems to solve when building tram systems.
| Challenge Category | Specific Issues | Potential Solutions |
| Infrastructure Integration | Fitting tracks into existing urban landscapes | Advanced urban planning techniques |
| Technical Compatibility | Ensuring interoperability with existing transit systems | Standardized technical specifications |
| Maintenance Requirements | Specialized skills and equipment needed | Comprehensive training programs |
Cities need to find a smart way to solve these problems. They must mix new technology with smart money plans to build modern tram systems.

Geopolitical and Economic Factors Impacting the Tram System Market
The tram system market is changing due to complex global factors. Government policies, market rules, and economic factors shape how cities build their transport systems.
World governments see the value in green transport options. They invest in trams because of economic needs and rules.
Key Economic Influences on Tram Systems
- Geopolitical tensions affecting global fuel prices
- Economic stability through alternative transportation solutions
- Strategic investments in urban mobility infrastructure
Studies show how the tram market stays strong. Geopolitical issues with oil countries like Russia, Iran, and Venezuela add uncertainty. This makes governments look for steady transport options.
| Economic Factor | Impact on Tram Systems | Potential Response |
| Oil Price Volatility | Increased transportation costs | Enhanced tram system investments |
| Global Economic Uncertainty | Reduced infrastructure spending | Cost-effective public transit solutions |
| Geopolitical Tensions | Market investment hesitation | Diversification of transportation infrastructure |
Government Policies Driving Market Growth
Government actions help tram systems grow. Rules support investing in city transport. The push for green travel boosts tram system growth.
Urban transportation is no longer just about moving people—it’s about creating sustainable, economically viable mobility solutions.
Market Segmentation: Types and Applications of Tram Systems
The tram system market is a complex mix of transportation technologies. It aims to meet the varied needs of urban mobility. Market segmentation shows how different tram technologies and urban uses are innovated and specialized.
Tram technologies have evolved to tackle specific urban transport challenges. This has created a strong market with many segment types:
- Articulated Trams: Flexible design for crowded urban corridors
- Double-Decker Trams: Enhanced passenger capacity
- Rubber-Tired Trams: Improved maneuverability
- Restaurant Trams: Unique urban entertainment experiences
Analysis of Different Tram Technologies
The tram technologies market shows a lot of difference across segments. Straddle monorail systems are leading, with a 69.6% market share by 2025. These systems use advanced sensors and software tailored for specific railway needs.
| Tram Type | Key Features | Primary Application |
| Articulated Tram | Modular design | Urban public transport |
| Double-Decker Tram | High passenger capacity | Dense metropolitan areas |
| Rubber-Tired Tram | Enhanced flexibility | Mixed urban environments |
Diverse Applications in Urban and Suburban Settings
Tram systems have two main uses in cities: commercial and industrial. Commercial uses focus on public transport. Industrial uses handle goods transport in complex facility networks.
“Tram technologies are reshaping urban mobility, offering sustainable and efficient transportation solutions,” says a leading urban transportation expert.
North American markets are expected to lead in revenue, thanks to ongoing innovation and strategic product launches. The Asia Pacific region is set for the fastest growth, driven by government demands for advanced transport infrastructure.
Tram Systems in Sustainable Transport and Urban Development
Urban mobility is evolving rapidly, with trams at the forefront of eco-friendly transportation solutions. This shift towards sustainable transport not only benefits the environment but also contributes to urban development. According to industry projections, the tram rail market is expected to experience significant growth, reaching a value of $40 billion by 2028.
Why Trams Matter in City Planning
Trams play a crucial role in shaping cities and their transportation systems. Here’s why they are so important:
- Environmental Impact: Trams have a lower carbon footprint compared to cars and buses. By promoting the use of trams, cities can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
- Efficient Transportation: Trams are designed to carry a large number of passengers at once, making them an efficient mode of transport for densely populated areas. They can help alleviate traffic congestion and improve overall mobility within cities.
- Sustainable Urban Development: The presence of tram systems can influence urban development patterns. Areas with access to trams tend to attract businesses, residents, and investments, leading to more sustainable growth.
As cities strive for greener and more sustainable futures, trams will continue to play a vital role in shaping urban mobility and reducing environmental impact.
Environmental Benefits of Tram Systems
- Dramatically reduced greenhouse gas emissions
- Minimal noise pollution compared to traditional transportation
- Enhanced air quality in urban environments
- Decreased reliance on individual automobile transportation
Urban Planning and Land Use Integration
Cities around the world see trams as essential for smart planning. Transit-oriented development is a big trend, with trams driving green growth and changing cityscapes.
Tram systems are not just transportation infrastructure—they are urban transformation engines.
New tech like automated trams and smart tickets are taking tram systems to the next level. Companies like Bombardier, Alstom, and Siemens are leading the charge, making green transport better and more accessible.
Future Outlook
As cities grow larger, trams will play a crucial role in creating environmentally friendly and connected urban areas. The expansion of tram systems in countries like Germany, Australia, and the United States demonstrates a worldwide movement towards sustainable transportation options.
Global Overview of the Tram System Market: Market Leaders and Key Regions
The global tram system market is full of innovation and new ways to move people around cities. Leaders in the market are making big moves with new tech and big projects. Regional transportation networks show how important trams are for city travel.
Looking at the market, we see some key points about growth and performance:
- North America leads with 37.7% market share by 2025
- Asia Pacific is growing the fastest
- European markets are investing a lot in their tram systems
Analysis of Major Market Players
The market is filled with big names in tram technology. These companies are working on green solutions that help cities and cut down on pollution.
| Region | Market Share | Growth Projection |
| North America | 37.7% | High |
| Asia Pacific | 25.3% | Rapid |
| Europe | 22.5% | Steady |
Regional Market Dynamics and Growth Projections
New markets are getting a lot of money for their city transport. Growth projections show tram systems will grow a lot, thanks to more people moving to cities and wanting to be green.
The future of city travel is about being smart, efficient, and good for the planet.
Germany's Dominance and Innovations in Tram System Development
Germany leads the world in tram system technology. It sets high standards for urban transportation. The country’s tram systems are known for their efficiency and cutting-edge tech.
Germany is all about pushing the limits of urban transport. Its tram makers focus on making systems that are green, comfy for riders, and run smoothly.
Historical Leadership in Urban Transportation
Germany’s tram network is a treasure trove of history. It has the biggest tram network in Europe. It links big cities with a well-built system.
- Pioneered modular tram design concepts
- Developed advanced electric propulsion systems
- Created intelligent traffic management technologies
Technological Advancements and Global Market Position
German tram makers are at the top thanks to their hard work in research. They sell their advanced tram systems all over the world.
| Technology Category | Key Innovation | Global Impact |
| Propulsion Systems | Electric Hybrid Drives | Reduced Carbon Emissions |
| Design Engineering | Lightweight Modular Constructions | Enhanced Efficiency |
| Smart Infrastructure | Integrated Digital Control Systems | Improved Urban Mobility |
Germany’s tech breakthroughs are changing how cities move. They show Germany’s unmatched skill in making top-notch tram systems.
Australia's Growing Demand for Tram Systems in Cities
Australia’s cities are evolving rapidly, and tram systems are becoming increasingly important in revitalizing urban areas. Melbourne and Gold Coast are at the forefront of this movement, implementing new tram networks that are transforming urban mobility.
The investments in transportation infrastructure in Australia indicate significant opportunities for expanding tram networks. In May 2019, the government announced ambitious plans to overhaul urban transit, signaling a clear commitment to promoting environmentally friendly transportation options.
Urban Renewal Projects and Network Expansions
Urban renewal projects in Australia show the power of tram systems:
- The Gold Coast Light Rail PPP project shows the power of public-private partnerships.
- The Sydney Metro Northwest Project is growing the city’s transport network.
- Melbourne’s tram network is a great example for urban transit growth.
Challenges and Market Opportunities
Australian tram systems offer great market opportunities, but they face big challenges. Building tram systems needs a lot of money, technical skills, and smart city planning. Companies from home and abroad are looking to help shape Australia’s future transport.
The future of urban mobility in Australia lies in sustainable, integrated transportation solutions that connect communities efficiently and environmentally responsibly.
The U.S. Market for Tram Systems: Trends and Opportunities
The U.S. tram market is changing fast. Cities all over are looking to improve their public transport. They’re turning to streetcars as a key part of this effort.
Urban areas are changing how they see public transport. The rise of streetcars is more than just a new way to get around. It’s a big step towards making cities better and greener.
Revival of Streetcar Systems in American Cities
Some big cities are leading the way in bringing back streetcars:
- Portland, Oregon – started using modern streetcars
- Cincinnati, Ohio – expanded its downtown transit
- Washington D.C. – included streetcars in its transit plans
These cities demonstrate how funding can transform urban transportation.
Regulatory Environment and Funding Mechanisms
The U.S. tram market faces funding hurdles but finds new ways to overcome them:
- Federal grants for transit projects
- Partnerships between public and private sectors
- Investments from local governments
New ways to fund streetcars are key to making cities more connected and efficient.
“Streetcars represent the future of sustainable urban transportation” – Urban Mobility Research Institute
The push for tram systems is getting stronger. This bodes well for the future of public transport in the U.S.
Future Prospects for Tram Systems: Advancements in Technology and Infrastructure
The world of city travel is changing fast, thanks to new tram technologies. These innovations are making city travel better and more green. They’re creating efficient ways for people to get around.
At the heart of these changes is how trams fit into the bigger picture of city travel. Trams are now more than just a way to get from A to B. They’re key parts of a larger, smarter travel system.
Emerging Technologies in Tram Design and Operation
Many exciting new technologies are coming to tram systems:
- Autonomous driving capabilities for trams
- Advanced battery-powered electric propulsion systems
- Smart energy recovery mechanisms
- Real-time passenger information networks
Next-Generation Urban Mobility Solutions
The future of trams is all about working well with other travel options. Intelligent transit platforms will make it easy to switch between trams, bikes, and self-driving cars.
Technological innovation is transforming urban transportation from a fragmented system to a unified, intelligent mobility ecosystem.
Expect to see better routes, smart maintenance, and easier travel interfaces. These changes will make city travel smoother and more enjoyable.
Cities are getting smarter, and trams are leading the way. They’re key to building green, connected cities that are good for everyone and the planet.
Competitive Dynamics in the Tram System Industry
The tram system market is highly competitive. Companies like Bombardier, Alstom, Siemens, and CRRC are leading the way. They form strategic partnerships to advance technology and expand their reach. Each player brings its own strengths, with innovative approaches driving change.
- Škoda Transportation – Czech Republic
- Alstom – France
- Siemens Mobility – Germany
- CAF – Spain
- Hyundai Rotem – South Korea
- Stadler Rail – Switzerland
- Bombardier Transportation – Canada
- CRRC Corporation Limited – China
- Hitachi Rail – Japan
- ABB – Switzerland
Overall
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Global Tram System Market Report |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Segment by Type |
· Articulated Trams · Double-Decker Trams · Rubber-Tired Trams · Restaurant Trams |
| Segment by Application |
· Commercial · Industrial |
| Geographies Covered |
· North America (United States, Canada) · Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Russia) · Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan) · Southeast Asia (India) · Latin America (Mexico, Brazil) |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
The tram system market demonstrates robust growth potential, driven by urbanization, sustainability goals, and technological advancements. Key trends include the rising demand for electric and hybrid trams, government investments in public transport, and the integration of smart technologies.
Stakeholders, including manufacturers and urban planners, face opportunities and challenges. Cities are adopting trams to reduce congestion and emissions, while public-private partnerships unlock funding for infrastructure. However, high costs and land constraints require innovative solutions.
Global Tram System Market Report (Can Read by Free sample) – Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Tram System Market Analysis Overview
- Competitive Forces Analysis (Porter’s Five Forces)
- Strategic Growth Assessment (Ansoff Matrix)
- Industry Value Chain Insights
- Regional Trends and Key Market Drivers
- Vacuum Arc RemeltingMarket Segmentation Overview
Chapter 2: Competitive Landscape
- Global Tram Systemplayers and Regional Insights
- Key Players and Market Share Analysis
- Sales Trends of Leading Companies
- Year-on-Year Performance Insights
- Competitive Strategies and Market Positioning
- Key Differentiators and Strategic Moves
Chapter 3: Tram System Market Segmentation Analysis
- Key Data and Visual Insights
- Trends, Growth Rates, and Drivers
- Segment Dynamics and Insights
- Detailed Market Analysis by Segment
Chapter 4: Regional Market Performance
- Consumer Trends by Region
- Historical Data and Growth Forecasts
- Regional Growth Factors
- Economic, Demographic, and Technological Impacts
- Challenges and Opportunities in Key Regions
- Regional Trends and Market Shifts
- Key Cities and High-Demand Areas
Chapter 5: Tram System Emerging and Untapped Markets
- Growth Potential in Secondary Regions
- Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
Chapter 6: Product and Application Segmentation
- Product Types and Innovation Trends
- Application-Based Market Insights
Chapter 7: Tram System Consumer Insights
- Demographics and Buying Behaviors
- Target Audience Profiles
Chapter 8: Key Findings and Recommendations
- Summary ofTram System Market Insights
- Actionable Recommendations for Stakeholders
Access the study in MULTIPLEFORMATS
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1-866-739-3133
Email: infor@wkinformation.com
Key Technologies Used in Modern Tram Systems
Modern trams use a variety of technologies, including:
- Electrification: Trams are powered by electricity, making them more environmentally friendly compared to diesel-powered vehicles.
- Low-floor designs: This feature allows for easier boarding and alighting, making trams more accessible to people with disabilities and those carrying heavy items.
- Smart traffic systems: Trams can communicate with traffic signals and other infrastructure to optimize their routes and reduce delays.
- Real-time tracking: Passengers can track the location and arrival times of trams through mobile apps or digital displays at stations.
- Autonomous capabilities: Some tram systems are experimenting with self-driving technology to improve efficiency and reduce operating costs.
How do tram systems contribute to sustainable urban development?
Trams help cities by cutting down on carbon emissions and improving air quality. They support building cities around public transport and offer a green way to move people.
What are the main challenges in implementing tram systems?
Starting tram systems is difficult. It requires a significant amount of money, and it’s challenging to integrate them into the city. They also need to coordinate with other forms of transportation and require specialized skills to operate.
Which countries are leading in tram system development?
Germany, Australia, and the U.S. are leading the way. Germany is ahead in technology, Australia is expanding its tram networks, and the U.S. is reintroducing streetcars.
What funding mechanisms are used for tram system projects?
Tram projects get money from:
- Grants
- Public-private partnerships
- Bonds
They also get help from federal and international funds.
What emerging technologies are shaping the future of tram systems?
New technologies such as battery-powered trams, autonomous driving systems, and intelligent tracks are playing a significant role in shaping the future of tram systems. Additionally, there are advancements in energy-efficient power solutions and integration with new urban mobility systems.
How do tram systems impact urban planning?
Trams shape cities by encouraging public transport and reducing car use. They help cities grow in a green way and support compact designs.
What are the different types of tram systems?
There are several types of trams, including:
- Streetcars
- Light rail
- Low-floor trams
- Tourist trams
Additionally, there are tram-trains that operate in both cities and suburbs.
How are governments supporting tram system development?
Governments back trams with green policies, funding, and projects to cut carbon. They also support urban renewal and offer incentives for green transport.

